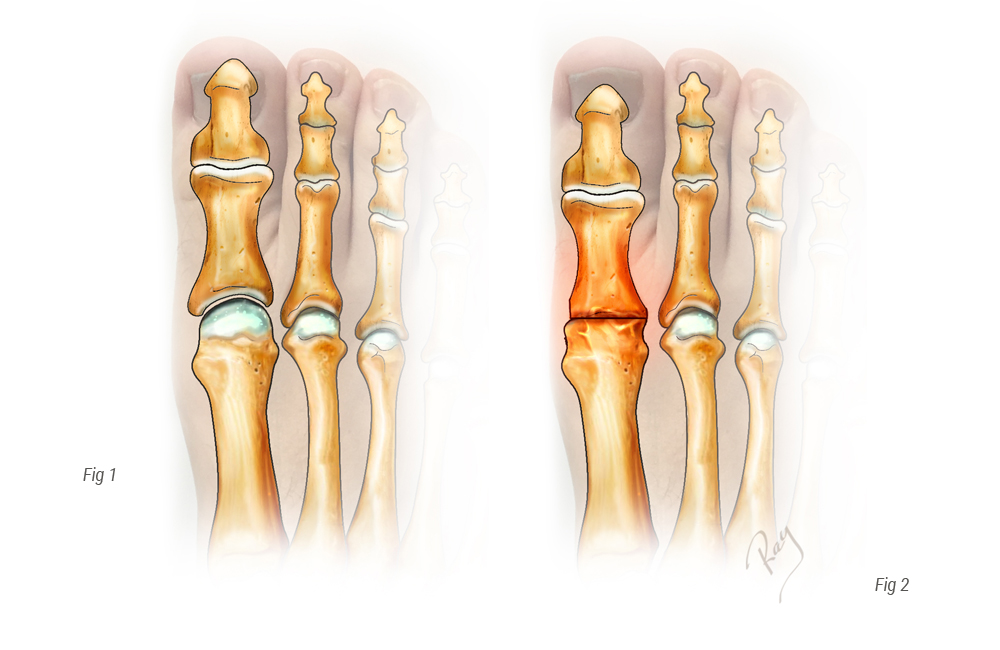
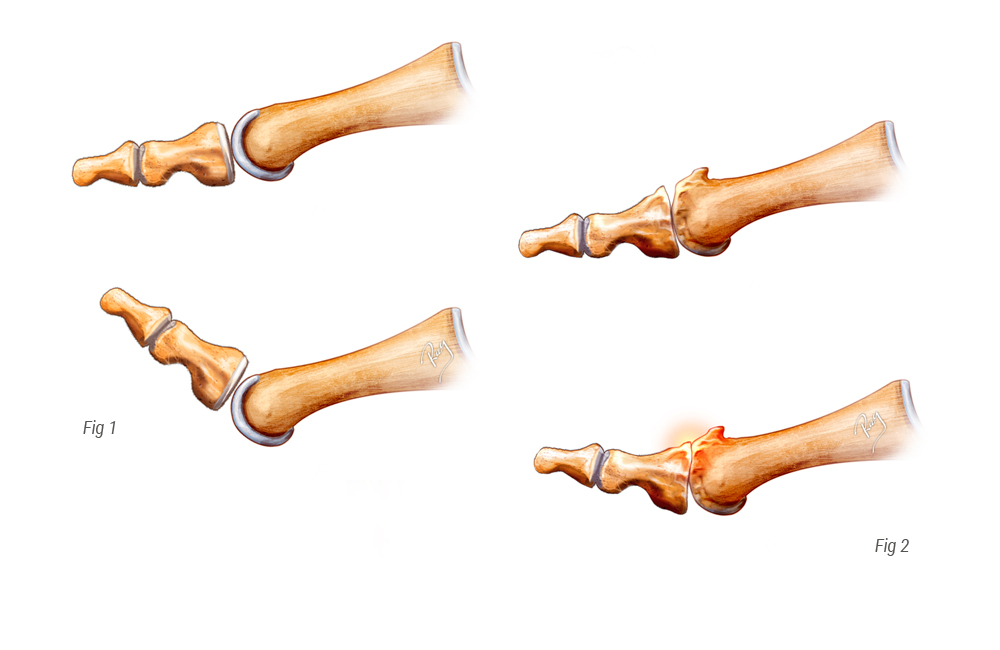
When conservative treatment is inadequate, surgery should be offered.
Several options are available depending on the degree of cartilage damage and the development of the osteophytes.
When the wear and tear to the cartilage is low or moderate and the main problem involves the osteophytes and the conflicts they entail, a simple excision can produce excellent results.
This technique, called cheilectomy, is typically performed by an open excision of the bony spurs. We prefer to perform this surgery percutaneously, meaning the size of the incision is 1 mm which facilitates the post-surgical recovery. This kind of surgery is sometimes completed by a procedure on the bone at the level of the phalanx, to further enhance the dorsiflexion mobility (osteotomy of the phalanx).
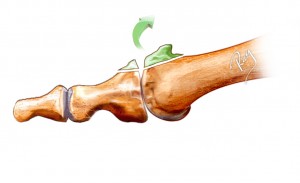
Cheilectomy: ablation of the excess bone (osteophyte) and its conflict
It is important to note that this technique does not alter the surface of the cartilage. Arthritis, and therefore the wear of the joint, progresses independently. This surgical procedure resolves the problem of the conflict related to the osteophytes and restores a certain amount of mobility to the big toe. It offers a temporary release from the pain, but it is sometimes sufficient to delay the final blocking of the joint (= arthrodesis) for many years. In fact, all joints are surrounded by a hard envelope, called a capsule, which is subject to tension from the osteophytes and increases the pressure on the joint. After a cheilectomy, this pressure is reduced and the constraints on the joint diminished.
When the injury to the cartilage is too significant, the preferred surgery is the final blocking of the joint. This procedure, called arthrodesis, consists of excising the remaining cartilage, placing the two bones into contact and fixing them with a plate or two screws. Contrary to popular opinion, the blocking of the joint has few repercussions on the quality of life and most patients can resume sport after healing (75-95% according to the sport). Wearing high heels can be a problem, but patients had usually stopped wearing such footwear prior to surgery, due to the loss of mobility caused by the arthritis.
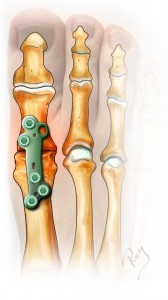
Arthrodesis with a plate
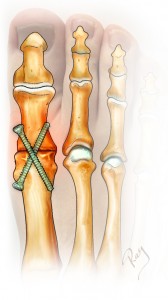
Arthrodesis with screws
As is the case with the hip, ankle or knee, joint replacements can be proposed for patients with advanced arthritis. The joint is replaced with a synthetic implant. The results obtained vary from one case to case and revision surgery, in the event of failure, can be complex. For this reason, arthrodesis is the preferred option for cases of severe arthritis, as it is extremely well tolerated and offers more reproducible results. However, a prosthesis remains a viable alternative.